
1、 Introduction to Ball Screw
Ball screws, precision components that efficiently convert rotary motion into linear motion or reverse linear motion into rotary motion, play a crucial role in the industrial field. Its core components include screws, nuts, steel balls, pre press plates, reversers, and dust collectors, each of which is carefully designed to ensure high performance and efficiency. The birth of this transmission component marks a significant transformation of bearings from sliding action to rolling action, thereby achieving low friction resistance and high-precision motion conversion. Therefore, ball screws play an indispensable role in machine tools and precision machinery, becoming a key component for achieving the conversion between rotation and linear motion, torque and axial force. Its main performance indicators include nominal diameter and lead, and the precise control of these parameters directly determines the transmission performance and service life of the ball screw.
2、 The working principle of ball screw
Ball screw, a precision component that efficiently converts rotational and linear motion, can be briefly summarized as follows: through the interaction between the nut and the screw, rotational motion is efficiently converted into linear motion, or vice versa. When the ball screw is used as the active body, the nut will convert into linear motion according to the corresponding lead as the screw rotates. The passive workpiece achieves corresponding linear motion through the connection between the nut seat and the nut. In addition, ball screw bearings provide diversified and standardized products to meet different needs, and their cycling and preloading methods can be selected according to specific applications. Screw rods are divided into two types: precision ball screws and cold-rolled ball screw bearings. The former undergoes high-precision grinding and processing, while the latter is formed by high-precision cold rolling, both with different precision levels for users to choose from.
3、 Diversified applications of ball screws
Ultra high DN value ball screws, due to their excellent performance, are often used in high-speed tool machines and high-speed integrated machining center machines to ensure high efficiency and precision machining requirements. End cap ball screw, compact and practical in design, is very suitable for applications in fast handling systems, general industrial machinery, and automation machinery. For CNC machinery, precision tool machines, industrial machinery, etc. that pursue high speed, high-speed ball screws are the ideal choice. In addition, precision grinding grade ball screws are widely used in various fields such as CNC machinery, precision tool machines, industrial machinery, electronic machinery, etc. Their high precision and high performance are favored by many users. The nut rotating (R1) series ball screw, with its unique design, has excelled in fields such as semiconductor machinery and industrial robots. Rolling grade ball screws have a place in the market due to their low friction, smooth operation, and fast and affordable supply advantages. For fully electric injection molding machines, stamping machines and other equipment that need to withstand heavy loads, heavy-duty ball screws can meet their demanding working environment requirements.
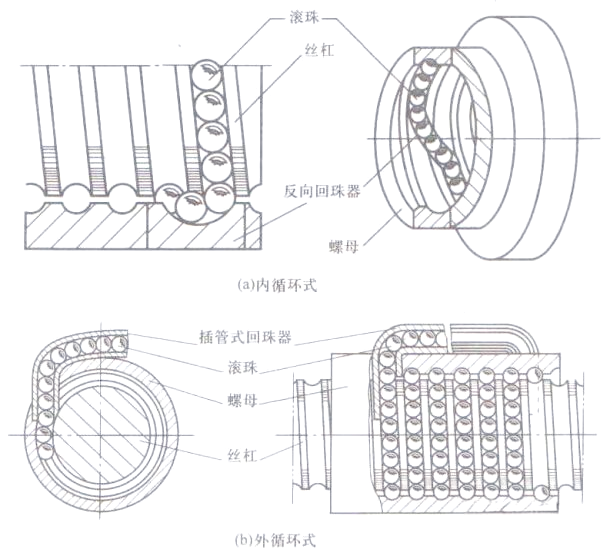
4、 Loop mode
The circulation of ball screws is usually divided into two types: external circulation and internal circulation. In the external circulation, the ball will temporarily detach from the screw during the circulation process; In the inner cycle, the ball always maintains continuous contact with the screw.
1) External circulation: After completing one cycle, the ball will pass through the spiral groove or insertion tube on the outer surface of the nut and return to the screw nut space to continue the next cycle. The return methods of external circulation ball screw nut pairs mainly include end cap type, insert tube type, and spiral groove type. End cap type is achieved by machining a longitudinal hole on the nut as a return channel, and the ball enters the return pipe through the return ports of the cover plates at both ends for circulation; The intubation type uses a bent pipe as the return pipe, which has good processability but larger radial dimensions; Spiral groove is milled out on the outer circle of the nut, and a return channel is formed by cutting the threaded raceway through the through holes drilled at both ends. Its radial size is small, but its manufacturing is more complex. The external circulation structure is simple and widely used, but the joint of the rolling track may affect the smoothness of the ball rolling track.
2) Internal circulation: Internal circulation is achieved through the use of a reversing device to circulate the balls. There are two types of reversing devices: cylindrical convex key reversing device and flat circular insert reversing device. The cylindrical part of the cylindrical convex key reverser is embedded in the nut, and the end is provided with a reverse groove, which is positioned through the outer circular surface of the cylinder and the circular key on it; The flat round block reversing device is a general round head flat key block, embedded in the cutting groove of the nut, with a reverse groove at its end, positioned by the outer contour of the block. The internal circulation structure is compact in size, but requires high precision in the dimensions of the external contour and the groove on the nut.
Type selection: The nuts of ball screws can be divided into bent pipe type, loop type, and end cap type according to the circulation mode of the steel ball. The bent nut circulates the steel ball through the bent pipe, and the steel ball is scooped from the groove of the screw shaft into the bent pipe and then returns to the groove for infinite cyclic motion; The circular nut uses a specialized circular device to circulate the steel ball. When selecting, suitable cycling methods and nut types can be chosen based on specific application and performance requirements.
These models of nuts are designed to be quite compact, cleverly changing the direction of the steel ball's movement using a cycler, allowing the steel ball to cross the outer diameter of the screw shaft and return to its original position, thereby achieving infinite cyclic motion.
In addition, end cap nuts (such as SBK, SDA, SBKH, WHF, BLK, WGF, BLW, WTF, CNF, and BLR types) are very suitable for high-speed feeding applications. In these nuts, the steel ball is cleverly scooped out of the groove of the screw shaft through the end cap, introduced into the through hole of the nut, and then returned to the groove through the through hole, achieving infinite cyclic motion.
5、 Characteristics
Low friction loss and high transmission efficiency
The design of the ball screw pair enables numerous balls to roll between the screw shaft and the screw nut, greatly improving the efficiency of motion. Compared to traditional sliding screw pairs, its driving torque is significantly reduced, up to 1/3, which means that the power required to achieve the same motion effect is greatly reduced, helping to save energy and electricity.
High precision
The production process of ball screw pairs is highly mechanized, and in various processes such as grinding, assembly, and inspection, the factory environment strictly controls temperature and humidity to ensure excellent product quality. This comprehensive quality management system ensures the accuracy of ball screw pairs is fully guaranteed.
High speed feed and micro feed capability
Due to the rolling motion characteristics of the ball screw pair, its starting torque is very small, avoiding the crawling phenomenon in sliding motion, thus achieving precise micro feed. This characteristic makes the ball screw pair perform well in high-speed feed.
High axial stiffness
Through preloading technology, the axial clearance of ball screw pairs can be eliminated, even reaching negative values, thereby significantly improving rigidity. This design enhances the rigidity of the mother part during actual use of the mechanical device, further optimizing the performance of the product.
Cannot self lock and has reversible transmission capability
In addition, ball screw pairs also have the characteristic of not being self-locking, which means that their transmission has reversibility. This characteristic makes ball screw pairs more flexible and versatile in applications.
6、 Protection of ball screw
Ball screw pairs enhance wear resistance and improve transmission efficiency through lubrication. Lubricants are mainly divided into two types: lubricating oil and lubricating grease. Lubricating oil is usually selected from engine oil, 90-180 turbine oil, or 140 spindle oil, while lithium based grease is often used as lubricating grease. Lubricating grease is applied to the threaded raceway and the housing space where the nut is installed, while lubricating oil is injected into the nut space through the oil hole on the housing.
To ensure long-term wear free operation of ball screw pairs and other rolling friction transmission components, it is necessary to prevent abrasive particles and chemically active substances from entering. However, if impurities are mixed into the raceway or unclean lubricating oil is used, it will hinder the normal operation of the ball bearings and cause rapid wear and tear.
Nut pairs are often sealed with felt rings, with a thickness of about 2-3 times the pitch. The inner hole is designed in a threaded shape to tightly wrap around the screw and fit into the slot holes at both ends of the nut or sleeve. In addition, oil resistant rubber or nylon materials can also be used to make sealing rings. It should be noted that due to the direct contact between the sealing ring and the screw, although the dust-proof effect is enhanced, it also increases the frictional resistance torque. To avoid this problem, a non-contact labyrinth seal ring made of hard plastic can be used, with its inner hole opposite the screw thread raceway and leaving appropriate clearance.
For exposed lead screws, spiral steel strips, telescopic sleeves, conical sleeves, and foldable plastic or synthetic leather protective covers are often used to prevent dust and abrasive particles from adhering to the surface of the lead screw. These protective covers are connected at one end to the end face of the ball nut and fixed at the other end to the support seat of the ball screw, ensuring a more stable protective effect.
7、 Key dimensions of threads
Thread is an important component of ball screw pairs, and its dimensional parameters have a significant impact on the performance and service life of ball screws. These key dimensions include thread diameter, pitch, and thread profile. When designing and selecting ball screws, it is necessary to fully consider the reasonable combination and selection of these parameters to ensure that the ball screw can meet practical usage needs.
)Outer diameter d (major diameter) (D) - This is the diameter of an imaginary cylindrical surface that coincides with the external thread crest, also commonly referred to as the nominal diameter.
)Inner diameter (small diameter) d1 (D1) - It coincides with the external thread root and is used as the calculated diameter of the dangerous section in strength calculations.
)Medium diameter d2- the imaginary diameter of a cylindrical surface in the axial section where the tooth thickness is equal to the interdental width, which approximates the average diameter of a thread. The calculation formula is d2 ≈ 0.5 (d+d1).
)Pitch P - This is the axial distance between two adjacent teeth on the generatrix of the center diameter cylindrical surface corresponding to two points.
)Lead (S) - the axial distance between two adjacent teeth on the same helical line on the generatrix of the center diameter cylindrical surface, and the relationship with the pitch is S=nP.
)Line number n - the number of spiral threads, usually for ease of manufacturing, the value of n does not exceed 4.
)Spiral Rise Angle PSI - This is the angle between the tangent of the helix on the center diameter cylindrical surface and the plane perpendicular to the helix axis.
8) Tooth profile angle α - the angle between the two sides of the thread profile in the axial plane of the thread.
9) Tooth profile inclination angle β - the angle between the side of a threaded tooth profile and the perpendicular plane of the thread axis, suitable for symmetrical tooth profiles.
In addition, for the main geometric dimensions of various threads (except rectangular threads), relevant standards can be consulted. It should be noted that the nominal size is usually approximately equal to the outer diameter of the thread, while for pipe threads, it is approximately equal to the inner diameter of the pipe.